Tech
1 day ago
Your Reach with Email Marketing Services in Dubai and UAE
In today’s online age, email marketing remains one of the best tools for reaching and…
Lifestyle
4 days ago
Why Wear Garnet Stone? Know Benefits!
The Natural Garnet is one of the foremost powerful and broadly hailed gemstones that represent…
Health
4 days ago
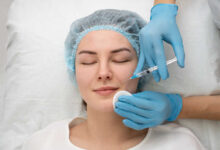
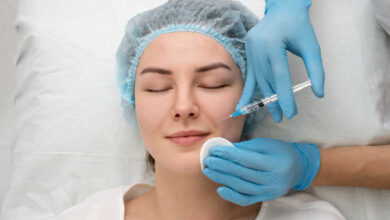
The Science Behind Facelift Treatments
Advances in facelift procedures have brought together scientific accuracy and artistic elegance in a beautiful…
Tech
4 days ago
How Is ASP.NET Different From Laravel: Key Factors
The framework you select in the discipline of web development can have a significant influence…
Tech
3 weeks ago
How Accessibility Testing Services Can Benefit Your Business?
In the constantly evolving dynamic landscape, you should be aware of the loopholes users face.…
Tech
3 weeks ago
Maximizing Business Benefits with Enterprise CRM Solutions
In today’s changing business landscape, the importance of enterprise CRM solutions cannot be just neglected. These…
Education
4 weeks ago
From Anywhere to Everywhere: How Online GMAT Training Opens Doors
Online GMAT schooling has revolutionized the manner aspiring enterprise school college students put together for…
Lifestyle
4 weeks ago
Properties and Benefits of Kyanite Stone
Kyanite is a stone that exhibits high energy and incredible healing properties. It gets its…
Tech
4 weeks ago
The Role of UI/UX in Enhancing Mobile App Engagement
Just imagine. Have you ever opened a website and within just a few seconds, you closed…
Tech
March 20, 2024
How to Boost Customer Satisfaction at Your Computer Repair Shop
Maintaining a profitable computer repair shop involves balancing technical know-how, efficiency, and top-notch customer support.…